by
The DermEngine Team on Dec 26, 2018
The concept of big data is becoming increasingly familiar across many fields of human activity.1 Data mining in numerous disciplines has become a source of enormous amounts of information, a trend that has also reached healthcare. The vast amounts of data collected are helping to draw behavioural patterns able to support future disease management. This article will look to describe the operational capacity and utility of big data for refined dermatology services that predict disease developing traits and contribute to an improved healthcare experience.
1. The nature and utility of big data
Although a frequently utilized term in technological fields, big data is not always as transparent in its definition as other emerging concepts such as artificial intelligence (AI) or machine learning. In fact, in the healthcare environment the development of more intricate digital health initiatives has contributed to the expansion of big data strategies making it more noticeable although not necessarily fully understood by all involved stakeholders.
As a broad definition, big data includes the collection and analysis of large amounts of information with the purpose of drawing emerging patterns that can help predict consistent behavioural traits.2 The real value of this approach lies in the astronomical volume of information being produced and collected in recent times. 2017 was the single year where more data was produced than in the previous 5,000 years of recorded human history.3
This impressive amount of information is being generated from a myriad of different sources where technology has some kind of influence, such as social media channels, GPS devices, sensors for industrial machinery operations, transactional and web data, cloud-based data collection services and others.4 In healthcare, the advent of intelligent electronic medical record (EMR) software has been the leading cause of patient data collection and analysis. The growing number of healthcare practitioners that rely on these systems to acquire and store data is probably the largest patient information source in recent times.5
Despite being a great technical challenge to collect, handle and analyze such large amounts of information, the dedicated work of specialized engineers is proving a good example of how as a species we can learn from the past to adapt for a better future. Healthcare disciplines have greatly benefited from the capacity of big data to unfold the potential contained in data and how it can be utilized to feed AI-driven algorithms able to make intelligent decisions for improved disease diagnosis and management.

2. Big data as the driving force for precise dermatology services
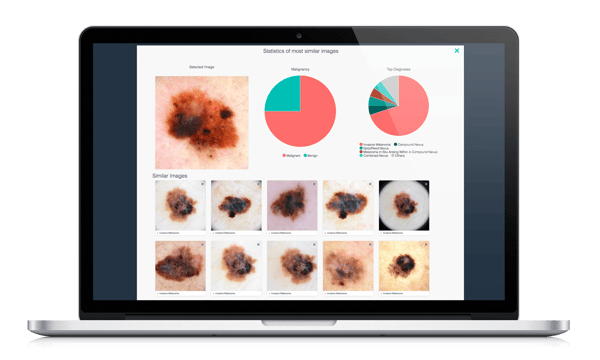
The power of big data analysts to draw conclusions from behavioural patterns acquired over large amounts of data provides an excellent way to leverage accurate responses for a variety of diseases. In dermatology, the work of engineers can be supplemental to the developments in AI, where algorithms can interpret data to make accurate predictions. Such case is the Visual Search feature present in the intelligent dermatology software DermEngine. The compilation of millions of pathologically pre-labelled skin lesion images can be used to build the databases from which machines learn and remember common disease traits. When compared to a target image, this system can assist in clinical diagnosis by providing an accurate prediction of the lesion’s nature, an image comparison process known as Content Based Image Retrieval (CBIR).
The potent combination of data analysis interpretation and machine learning is bringing new mechanisms to automate highly complex and specific tasks, able to be performed by AI-led systems with a degree of accuracy higher than human standards. The real value of big data is based on the potential of leveraging unprecedented volumes of disease population statistic data to shed light on behavioural patterns common to the vast majority of dermatology case studies. To this regard, big data plays a pivotal role in healthcare as it can provide the resources to better understand disease development, allowing for efficient responses and higher survival chances. For melanoma and other skin cancer types, understanding the nature of the disease to respond with a decisive action plan constitutes a life-saving approach. On the other hand, data also represents the driving force to automate time-consuming processes where machines are less prone to error compared to humans, therefore leaving doctors with more time to focus on their relationships with patients.6
Conclusion
Technology has brought transformative changes in healthcare, many of which were unthinkable some decades ago. In fact, the pace of newer developments in big data and AI are causing profound transformations in dermatology as one of several health-related disciplines. The large scale predictability derived from big data analysis is providing the tools to understand diseases behavioural patterns that are vital to successfully counteract them. As time goes by and data continues to accumulate, intelligent algorithms equipped with the latest datasets will help identify the traits leading to skin cancer early detection providing higher survival rates and a streamlined healthcare experience for patients.
-The MetaOptima Team
Would you like to stay updated on the latest news of MetaOptima and its dermatology solution, DermEngine? Subscribe to our blog below! If you're ready to experience DermEngine's intuitive features for yourself, sign up for a demo today!

Sources
1-https://www.import.io
2-https://www.sas.com
3-https://appdevelopermagazine.com
4-https://blog.microfocus.com
5-https://www.healthcareitnews.com
6-https://www.medicaldevice-network.com







